Tuberculosis (Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Risks)
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs but can also impact other parts of the body, such as the kidneys, spine, and brain. TB spreads through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or speaks, releasing bacteria into the air that others can inhale.
Symptoms of Active TB Disease:
- Persistent Cough: A cough lasting more than three weeks, sometimes producing blood or sputum.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain during breathing or coughing.
- Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness or weakness.
- Fever and Night Sweats: Elevated body temperature accompanied by sweating during the night.
- Unintended Weight Loss: Losing weight without trying.
These symptoms can be mild for many months, leading to delays in seeking care and increasing the risk of transmission.
Diagnosis:
If TB is suspected, healthcare providers may use several diagnostic methods:
- Rapid Molecular Tests: Recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) as the initial diagnostic test for individuals showing signs of TB.
- Sputum Tests: Analyzing mucus from the lungs to detect TB bacteria.
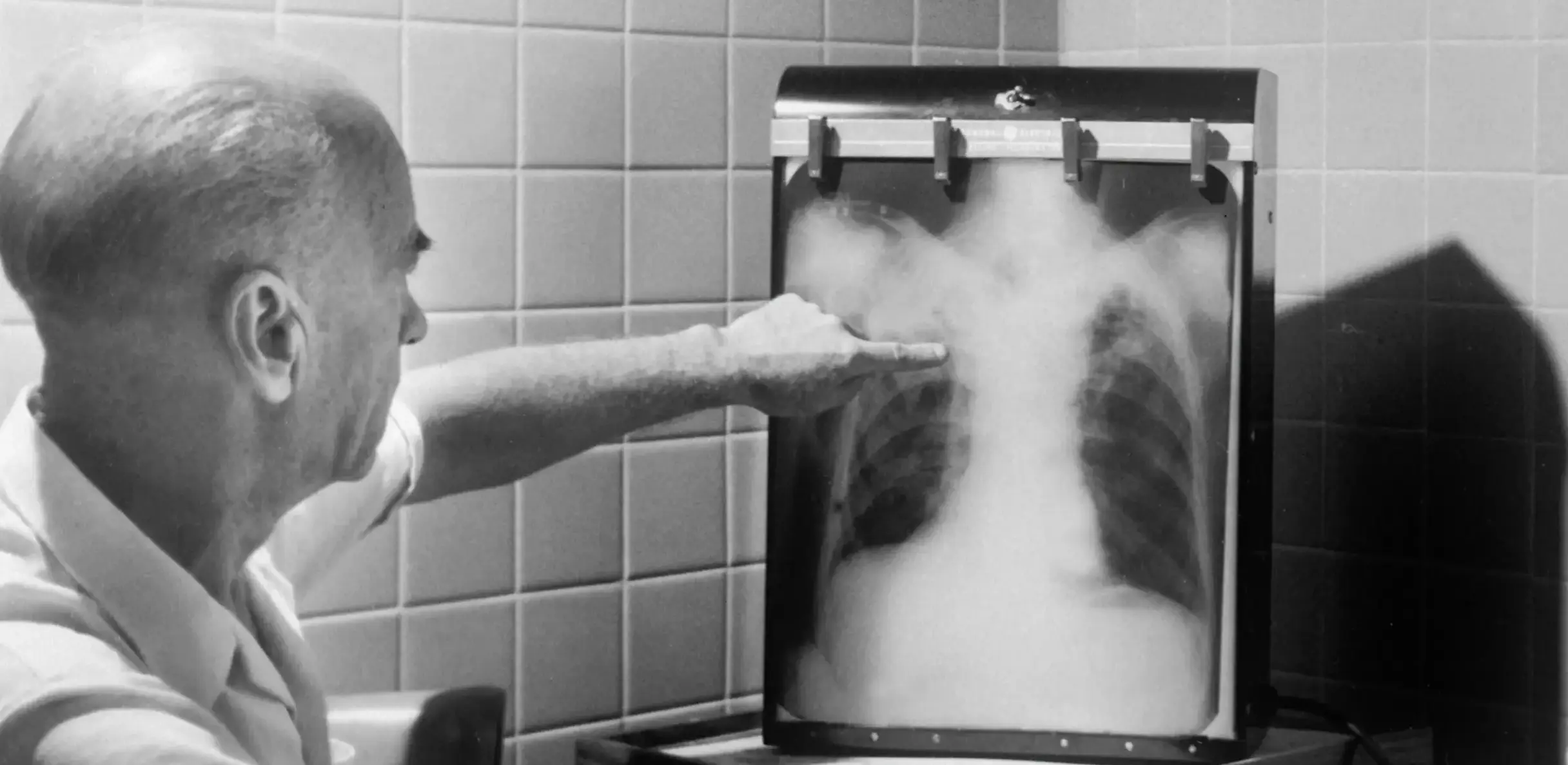
- Chest X-rays: To identify lung abnormalities caused by TB.
For latent TB infection, skin tests or blood tests can identify the presence of TB bacteria in the body.
Treatment:
TB is curable with proper treatment. The standard regimen involves a combination of antibiotics taken over a period of 6 to 9 months. Common medications include isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. It’s crucial to complete the full course of treatment to prevent the development of drug-resistant TB strains.
Prevention:
- Early Detection: Seek medical attention if you experience symptoms like a prolonged cough, fever, or unexplained weight loss.
- Testing: Individuals at increased risk, such as those with HIV or close contacts of TB patients, should get tested.
- Good Hygiene: Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and dispose of tissues properly.
- Vaccination: The Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine offers protection against TB and is recommended in countries with high TB prevalence.
Tuberculosis (TB) cases in the United States have seen a notable increase in recent years. In 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported 9,633 TB cases, marking the highest count since 2013. This represents an 8.3% rise compared to 2019, with an incidence rate of 2.9 cases per 100,000 persons.
A significant outbreak occurred in Kansas, particularly in Wyandotte and Johnson counties, where 67 active TB cases and 79 latent infections were reported since 2024. This has been described as the largest documented TB outbreak in the U.S. since the CDC began monitoring the disease in the 1950s.
TB is an airborne disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs. Symptoms include persistent cough, chest pain, and fatigue. While treatable with antibiotics, the treatment regimen is extensive, typically lasting several months. Health officials emphasize the importance of early detection and adherence to treatment protocols to prevent further transmission.
Despite these outbreaks, TB remains relatively rare in the U.S., often spreading in close-contact environments. The CDC continues to work with local health departments to manage and contain these outbreaks, ensuring public health safety.
Tuberculosis Symptoms
TB symptoms vary depending on the part of the body affected. However, the most common signs include:
- Persistent cough lasting more than three weeks
- Coughing up blood or mucus
- Chest pain during breathing or coughing
- Unexplained weight loss
- Night sweats
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite
What is the First Sign of Tuberculosis?
The first noticeable sign of TB is usually a prolonged cough accompanied by fatigue and mild fever. Many people mistake these early symptoms for a common cold, delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of TB in Adults
TB symptoms in adults are often more pronounced due to weakened immunity. Common signs include:
- Severe coughing with blood-stained sputum
- Chest pain that worsens over time
- Difficulty breathing
- Unexplained fever and night sweats
- Sudden weight loss
- Swelling in lymph nodes
Symptoms of Tuberculosis in the Throat
Throat TB, also known as laryngeal TB, affects the voice box and throat. It is rare but highly contagious. Symptoms include:
- Hoarseness or loss of voice
- Persistent sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Blood in saliva or phlegm
Tuberculosis Causes
TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which spreads through airborne droplets. The risk of infection increases with:
- Close contact with an infected person
- Weak immune system due to HIV, diabetes, or malnutrition
- Living in crowded or unsanitary conditions
- Smoking or excessive alcohol consumption
- Chronic lung diseases
How Does TB Kill You?
If untreated, TB can be fatal. The bacteria destroy lung tissues, leading to respiratory failure. In severe cases, TB spreads to the brain, spine, or kidneys, causing organ failure. Multi-drug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) is even more dangerous, as it resists common antibiotics.
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Symptoms
Pulmonary TB affects the lungs and is the most common form. Symptoms include:
- Chronic cough with bloody mucus
- Severe chest pain and difficulty breathing
- Continuous fever and chills
- Night sweats and fatigue
- Rapid weight loss
Which Type of TB is Dangerous?
TB is classified into:
| Type of TB | Description | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Latent TB | No symptoms, bacteria inactive | Low |
| Active TB | Symptoms present, contagious | High |
| Pulmonary TB | Affects the lungs, the most common | High |
| Extrapulmonary TB | Affects other organs | Varies |
| MDR-TB (Drug-resistant TB) | Resistant to antibiotics | Very High |
| XDR-TB (Extensively Drug-Resistant TB) | Resistant to multiple drugs | Extremely High |
Tuberculosis Treatment

TB treatment requires antibiotics taken over 6–9 months. The most common medications include:
- Isoniazid (INH)
- Rifampin (RIF)
- Ethambutol (EMB)
- Pyrazinamide (PZA)
Tips for Successful TB Treatment:
- Take medications regularly as prescribed.
- Complete the full treatment course.
- Maintain a healthy diet and avoid smoking.
- Stay in well-ventilated areas to prevent the spreading TB.
Conclusion
Tuberculosis remains a serious global health concern, but early diagnosis and proper treatment can prevent severe complications. If you experience persistent cough, weight loss, or fever, consult a doctor immediately. Learn more about health and wellness at 4cintegratedhealth.com and share your thoughts in the comments below.